Money and Banking (मुद्रा और बैंकिंग)
(From NCERT Introductory Macroeconomics – 2025–26 Edition)
🌟 Chapter Summary / अध्याय सारांश
English:
Money is anything that is universally accepted as a medium of exchange, a measure of value, a store of value, and a standard of deferred payments.
This chapter explains the evolution, functions, and supply of money, as well as the role of commercial banks and the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in credit creation and controlling the money supply in the economy.
Hindi:
मुद्रा (Money) वह वस्तु है जिसे समाज सामान्यतः विनिमय के माध्यम, मूल्य की माप, मूल्य का संचय, और स्थगित भुगतान के मानक के रूप में स्वीकार करता है।
इस अध्याय में मुद्रा का विकास, इसके कार्य, मुद्रा आपूर्ति (Money Supply) की माप, तथा वाणिज्यिक बैंकों (Commercial Banks) और भारतीय रिज़र्व बैंक (RBI) की भूमिका को समझाया गया है।
🔑 Key Concepts / प्रमुख अवधारणाएँ
| Concept | Explanation (English) | व्याख्या (Hindi) |
|---|---|---|
| Money | Anything generally accepted as a medium of exchange. | वह वस्तु जो विनिमय के माध्यम के रूप में स्वीकार की जाती है। |
| Barter System | Exchange of goods for goods without money. | बिना मुद्रा के वस्तु-विनिमय की प्रणाली। |
| Double Coincidence of Wants | Both parties need what the other has. | दोनों पक्षों की आवश्यकताएँ एक-दूसरे से मेल खाएँ। |
| Fiat Money | Money issued by government order (legal tender). | सरकार द्वारा वैध घोषित मुद्रा। |
| Demand Deposits | Deposits that can be withdrawn on demand. | बैंक खाते में जमा धन जिसे माँग पर निकाला जा सकता है। |
| Money Supply (M1–M4) | Total stock of money in the economy at a given time. | अर्थव्यवस्था में किसी समय पर उपलब्ध कुल मुद्रा मात्रा। |
💰 Functions of Money / मुद्रा के कार्य
Primary Functions (प्राथमिक कार्य):
1️⃣ Medium of Exchange (विनिमय का माध्यम) – Eliminates the problem of barter.
2️⃣ Measure of Value (मूल्य की माप) – Common unit to express value of goods/services.
Secondary Functions (गौण कार्य):
1️⃣ Store of Value (मूल्य का संचय) – Can be saved and used in future.
2️⃣ Standard of Deferred Payment (स्थगित भुगतान का मानक) – Future payments are made in money terms.
3️⃣ Transfer of Value (मूल्य का स्थानांतरण) – Facilitates transfer of purchasing power.
⚙️ Money Supply in India / भारत में मुद्रा आपूर्ति
Defined by RBI:
| Measure | Components | Hindi Description |
|---|---|---|
| M1 (Narrow Money) | Currency with public + Demand deposits + Other deposits with RBI | संकीर्ण मुद्रा – नकद व चालू खाते की जमा राशि |
| M2 | M1 + Post office savings deposits | M1 में डाकघर की बचत जमा जोड़ें |
| M3 (Broad Money) | M1 + Time deposits with banks | व्यापक मुद्रा – M1 + सावधि जमा |
| M4 | M3 + Total deposits with post offices | M3 में डाकघर की कुल जमा जोड़ें |
👉 In India, M3 is the most commonly used measure of money supply.
Hindi: भारत में M3 को मुद्रा आपूर्ति का सबसे प्रमुख माप माना जाता है।
🏦 Commercial Banks / वाणिज्यिक बैंक
Functions of Commercial Banks:
1️⃣ Accepting Deposits
2️⃣ Providing Loans and Advances
3️⃣ Credit Creation
4️⃣ Agency Functions (cheques, drafts, remittances)
5️⃣ General Utility Services
Hindi:
वाणिज्यिक बैंक के कार्य हैं:
- जमा स्वीकार करना
- ऋण और अग्रिम प्रदान करना
- मुद्रा सृजन करना
- अभिकर्ता कार्य (चेक, ड्राफ्ट, भुगतान)
- सामान्य सेवाएँ देना
💸 Credit Creation by Commercial Banks / मुद्रा सृजन की प्रक्रिया
English Explanation:
Banks create money through the process of lending. They keep a portion of deposits as Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) and lend the rest. The loaned money, when redeposited, becomes the basis for further lending.
Money Multiplier = 1/CRR
Example:
If CRR = 20%, multiplier = 1 / 0.2 = 5 → ₹1,000 deposit creates ₹5,000 in money supply.
Hindi Explanation:
बैंक अपनी जमा राशि का एक भाग नकद आरक्षित अनुपात (CRR) के रूप में रखते हैं और शेष को ऋण के रूप में देते हैं। इस प्रक्रिया से नई मुद्रा का सृजन होता है।
मुद्रागुणक = 1/CRR
उदाहरण:
यदि CRR = 20%, तो मुद्रा गुणक = 5 होगा — ₹1,000 की जमा से ₹5,000 की मुद्रा का सृजन।
🏛️ Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and Its Functions / भारतीय रिज़र्व बैंक के कार्य
| Function | Explanation (English) | हिंदी विवरण |
|---|---|---|
| Issue of Currency | Monopoly right to issue currency except ₹1 notes and coins. | मुद्रा निर्गमन का एकाधिकार (₹1 नोट/सिक्का को छोड़कर)। |
| Banker to Government | Manages accounts, loans, and debt of government. | सरकार के खाते व ऋण का प्रबंधन। |
| Banker’s Bank | Lender of last resort to commercial banks. | वाणिज्यिक बैंकों का अंतिम ऋणदाता। |
| Controller of Credit | Controls credit using CRR, Repo Rate, SLR, etc. | CRR, SLR, रेपो दर आदि से ऋण नियंत्रण करता है। |
| Custodian of Foreign Exchange | Manages foreign currency reserves. | विदेशी मुद्रा भंडार का संरक्षक। |
📉 Instruments of Credit Control / ऋण नियंत्रण के उपकरण
| Type | Tools | English Explanation | हिंदी विवरण |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quantitative | CRR, SLR, Repo Rate, Reverse Repo, Open Market Operations | Affect the overall volume of credit. | कुल ऋण मात्रा को प्रभावित करते हैं। |
| Qualitative | Margin requirements, Credit rationing, Moral suasion | Affect distribution of credit. | ऋण वितरण को नियंत्रित करते हैं। |
🧾 Important Definitions / महत्वपूर्ण परिभाषाएँ
- Repo Rate: Interest rate at which RBI lends to commercial banks.
- Reverse Repo Rate: Rate at which RBI borrows from commercial banks.
- Bank Rate: Long-term lending rate by RBI.
- CRR (Cash Reserve Ratio): % of deposits banks keep with RBI.
- SLR (Statutory Liquidity Ratio): % of deposits banks must keep in liquid form (cash/gold).
Hindi:
- रेपो दर: वह दर जिस पर RBI वाणिज्यिक बैंकों को ऋण देता है।
- रिवर्स रेपो दर: वह दर जिस पर RBI बैंकों से धन उधार लेता है।
- बैंक दर: RBI द्वारा दीर्घकालिक ऋण पर ली जाने वाली दर।
- CRR: जमा का वह प्रतिशत जो बैंकों को RBI में रखना होता है।
- SLR: जमा का वह प्रतिशत जो बैंक नकद/सोने के रूप में रखते हैं।
🧮 Key Formulas / प्रमुख सूत्र
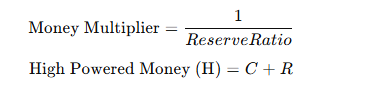
Where,
C = Currency held by public
R = Reserves with banks
📝 Important Questions / महत्त्वपूर्ण प्रश्न
English:
- Define money and its primary functions.
- What is the money supply? Explain M1 and M3.
- Explain the process of credit creation by commercial banks.
- State the main functions of RBI.
- Distinguish between Repo Rate and Reverse Repo Rate.
Hindi:
- मुद्रा की परिभाषा और उसके प्राथमिक कार्य बताइए।
- मुद्रा आपूर्ति क्या है? M1 और M3 को समझाइए।
- वाणिज्यिक बैंकों द्वारा मुद्रा सृजन की प्रक्रिया बताइए।
- भारतीय रिज़र्व बैंक के मुख्य कार्य लिखिए।
- रेपो दर और रिवर्स रेपो दर में अंतर बताइए।
📌 Keywords / मुख्य शब्दावली
Money – मुद्रा
Money Supply – मुद्रा आपूर्ति
Credit Creation – मुद्रा सृजन
RBI – भारतीय रिज़र्व बैंक
Repo Rate – रेपो दर
CRR – नकद आरक्षित अनुपात
Banking System – बैंकिंग प्रणाली
