Open Economy Macroeconomics (खुली अर्थव्यवस्था का व्यापक अर्थशास्त्र)
(From NCERT Introductory Macroeconomics – 2025–26 Edition)
🌟 Chapter Summary / अध्याय सारांश
English:
An open economy is one that engages in economic activities with other countries through trade, investment, and financial transactions. This chapter explains how foreign trade affects national income, introduces the concept of Balance of Payments (BOP), and discusses foreign exchange rates and their determination under different systems — fixed, flexible, and managed floating exchange rates.
Hindi:
खुली अर्थव्यवस्था वह होती है जो अन्य देशों के साथ व्यापार, निवेश और वित्तीय लेन-देन में भाग लेती है।
इस अध्याय में विदेशी व्यापार का राष्ट्रीय आय पर प्रभाव, भुगतान संतुलन (BOP) की अवधारणा, तथा विनिमय दर (Exchange Rate) के निर्धारण को विभिन्न प्रणालियों — स्थिर, परिवर्ती और नियंत्रित परिवर्ती — के अंतर्गत समझाया गया है।
🔑 Key Concepts / प्रमुख अवधारणाएँ
| Concept | Explanation (English) | व्याख्या (Hindi) |
|---|---|---|
| Open Economy | Economy engaged in international trade and capital flow. | वह अर्थव्यवस्था जो विदेशी व्यापार और पूँजी प्रवाह में संलग्न होती है। |
| Closed Economy | Economy with no foreign trade or exchange. | वह अर्थव्यवस्था जो विदेशी व्यापार नहीं करती। |
| Exports (X) | Goods and services sold to other countries. | अन्य देशों को बेची गई वस्तुएँ व सेवाएँ। |
| Imports (M) | Goods and services purchased from abroad. | विदेशों से खरीदी गई वस्तुएँ व सेवाएँ। |
| Net Exports (NX) | Exports – Imports | निर्यात – आयात का अंतर। |
| Balance of Payments (BOP) | Record of all international transactions. | सभी अंतरराष्ट्रीय लेन-देन का लेखा। |
| Exchange Rate | Rate at which one currency is exchanged for another. | वह दर जिस पर एक मुद्रा दूसरी मुद्रा में बदली जाती है। |
💱 National Income in Open Economy / खुली अर्थव्यवस्था में राष्ट्रीय आय
Y=C+I+G+(X−M)
Where:
Y = National Income
C = Consumption
I = Investment
G = Government Expenditure
X = Exports
M = Imports
Hindi:
खुली अर्थव्यवस्था में राष्ट्रीय आय का समीकरण:
Y=C+I+G+(X−M)
यहाँ (X – M) को Net Exports (शुद्ध निर्यात) कहा जाता है।
🏦 Balance of Payments (BOP) / भुगतान संतुलन
Structure of BOP:
1️⃣ Current Account – Exports and imports of goods & services, income, transfers.
2️⃣ Capital Account – Borrowings, investments, foreign exchange reserves.
Equilibrium in BOP:
When total receipts = total payments.
Deficit means payments > receipts; surplus means receipts > payments.
Hindi:
भुगतान संतुलन के दो मुख्य भाग होते हैं:
- चालू खाता (Current Account) – वस्तुओं, सेवाओं, आय और अंतरणों से संबंधित।
- पूँजी खाता (Capital Account) – विदेशी ऋण, निवेश और मुद्रा भंडार से संबंधित।
जब कुल प्राप्तियाँ = कुल भुगतान हों, तो BOP संतुलित होता है।
⚙️ Foreign Exchange / विदेशी मुद्रा
Meaning:
Foreign exchange refers to the foreign currency used for international payments.
Forex Market:
A market where currencies are bought and sold.
Participants:
- Central banks (like RBI)
- Commercial banks
- Exporters & importers
- Foreign investors
Hindi:
विदेशी मुद्रा वह विदेशी करेंसी है जिसका उपयोग अंतरराष्ट्रीय भुगतान में किया जाता है।
विदेशी मुद्रा बाजार (Foreign Exchange Market) वह स्थान है जहाँ मुद्राओं की खरीद-बिक्री होती है।
🔄 Exchange Rate Systems / विनिमय दर की प्रणालियाँ
| Type | Explanation (English) | हिंदी विवरण |
|---|---|---|
| Fixed Exchange Rate | Government fixes the value of currency. | मुद्रा का मूल्य सरकार द्वारा निर्धारित। |
| Flexible (Floating) Rate | Determined by market forces of demand & supply. | माँग और आपूर्ति के अनुसार तय होती है। |
| Managed Floating | Central bank intervenes occasionally to stabilize rate. | केंद्रीय बैंक कभी-कभी हस्तक्षेप करता है। |
💹 Determination of Exchange Rate (Demand–Supply Model) / विनिमय दर का निर्धारण
English:
- Demand for foreign exchange arises from imports, foreign travel, education, etc.
- Supply of foreign exchange comes from exports, foreign investment, remittances, etc.
- Equilibrium rate is determined where demand = supply.
Hindi:
- विदेशी मुद्रा की माँग – आयात, विदेशी शिक्षा, यात्रा आदि के कारण।
- विदेशी मुद्रा की आपूर्ति – निर्यात, विदेशी निवेश, प्रवासी धन भेजने आदि से।
- जहाँ माँग और आपूर्ति बराबर होती है, वहीं विनिमय दर संतुलित होती है।
💵 Depreciation and Appreciation / अवमूल्यन व मूल्यवृद्धि
| Term | Explanation (English) | हिंदी विवरण |
|---|---|---|
| Depreciation | Fall in value of domestic currency under flexible system. | लचीली प्रणाली में घरेलू मुद्रा के मूल्य में गिरावट। |
| Appreciation | Rise in value of domestic currency under flexible system. | लचीली प्रणाली में घरेलू मुद्रा के मूल्य में वृद्धि। |
| Devaluation | Deliberate reduction by government under fixed system. | स्थिर प्रणाली में सरकार द्वारा जानबूझकर मूल्य घटाना। |
| Revaluation | Deliberate increase in fixed exchange rate. | स्थिर विनिमय दर में जानबूझकर मूल्य बढ़ाना। |
🌍 Role of Foreign Exchange Market / विदेशी मुद्रा बाजार की भूमिका
1️⃣ Facilitates international payments.
2️⃣ Helps in conversion of currencies.
3️⃣ Determines exchange rate.
4️⃣ Provides hedging against currency risk.
Hindi:
- अंतरराष्ट्रीय भुगतानों को सुगम बनाता है।
- मुद्राओं के रूपांतरण में सहायता करता है।
- विनिमय दर का निर्धारण करता है।
- मुद्रा जोखिम से सुरक्षा प्रदान करता है।
🧾 Important Formulas / प्रमुख सूत्र
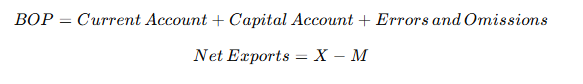
📝 Important Questions / महत्त्वपूर्ण प्रश्न
English:
- What is an open economy?
- Explain the meaning and components of Balance of Payments.
- What are the different types of exchange rate systems?
- Differentiate between depreciation and devaluation.
- Explain how foreign exchange rate is determined in the market.
Hindi:
- खुली अर्थव्यवस्था क्या है?
- भुगतान संतुलन की परिभाषा और घटक बताइए।
- विनिमय दर की विभिन्न प्रणालियाँ समझाइए।
- अवमूल्यन और अवमूल्यन में अंतर बताइए।
- विदेशी मुद्रा दर का निर्धारण कैसे होता है?
📌 Keywords / मुख्य शब्दावली
Open Economy – खुली अर्थव्यवस्था
Foreign Exchange – विदेशी मुद्रा
Exchange Rate – विनिमय दर
Balance of Payments – भुगतान संतुलन
Depreciation – अवमूल्यन
Appreciation – मूल्यवृद्धि
